Pelvic floor exercises in pregnancy

A strong pelvic floor can:
Your pelvic floor has an important role to play during pregnancy, birth and post-birth.
If you’re starting to get active for two by exercising in pregnancy, it’s well worth including pelvic floor exercises in your routine.
What is my pelvic floor?
The pelvic floor is a set of muscles attached to the base of your spine at the back, and your pubic bone at the front. These muscles act like a hammock, supporting your bowel, uterus and bladder, which all pass through this hammock. When you use the toilet, sneeze or lift a heavy object, your pelvic floor muscles contract to keep everything in place.
They also form the base of your core – the group of muscles which run from your pelvis to your diaphragm and are responsible for stability when exercising.
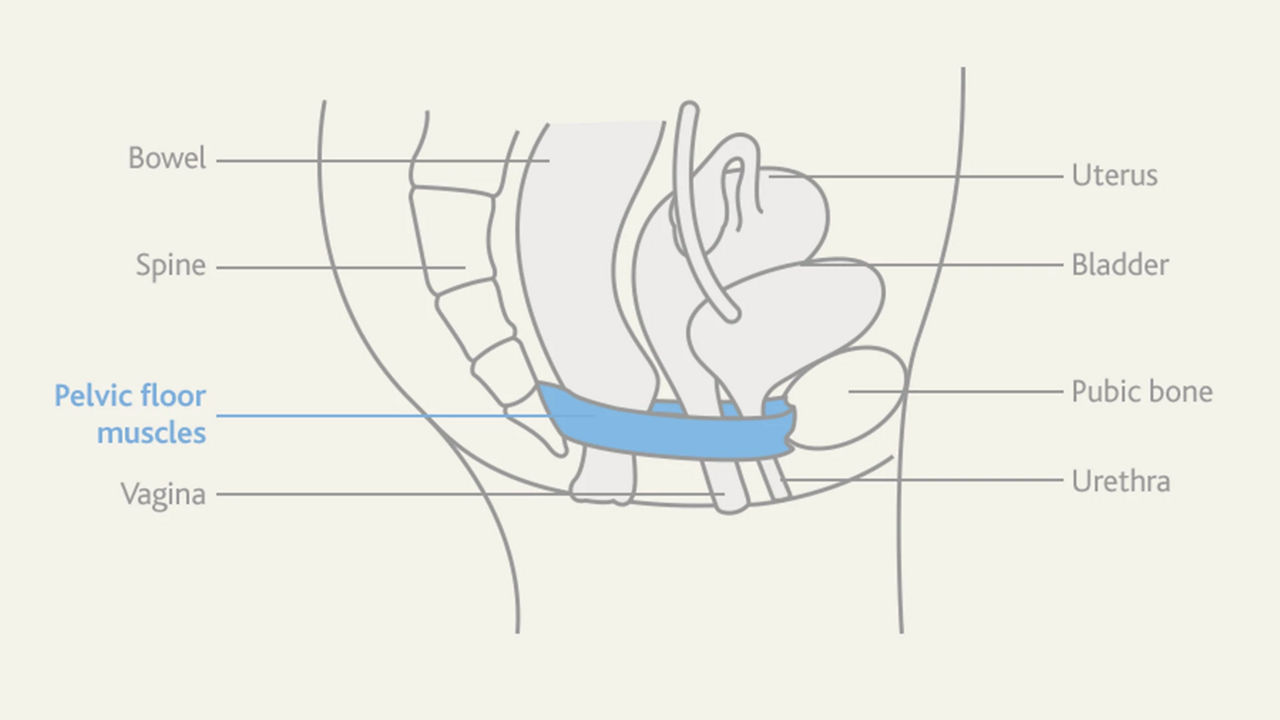
How to locate your pelvic floor
An easy way to locate your pelvic floor is by trying to stop mid-flow when you’re having a wee. The internal muscles you lift and clench to do this form your pelvic floor. It’s not advisable to do this regularly, though, as it can harm your bladder1.
How to do pelvic floor exercises
The most effective way to improve both the strength and stamina of your pelvic floor muscles is to combine both short and long squeezes.
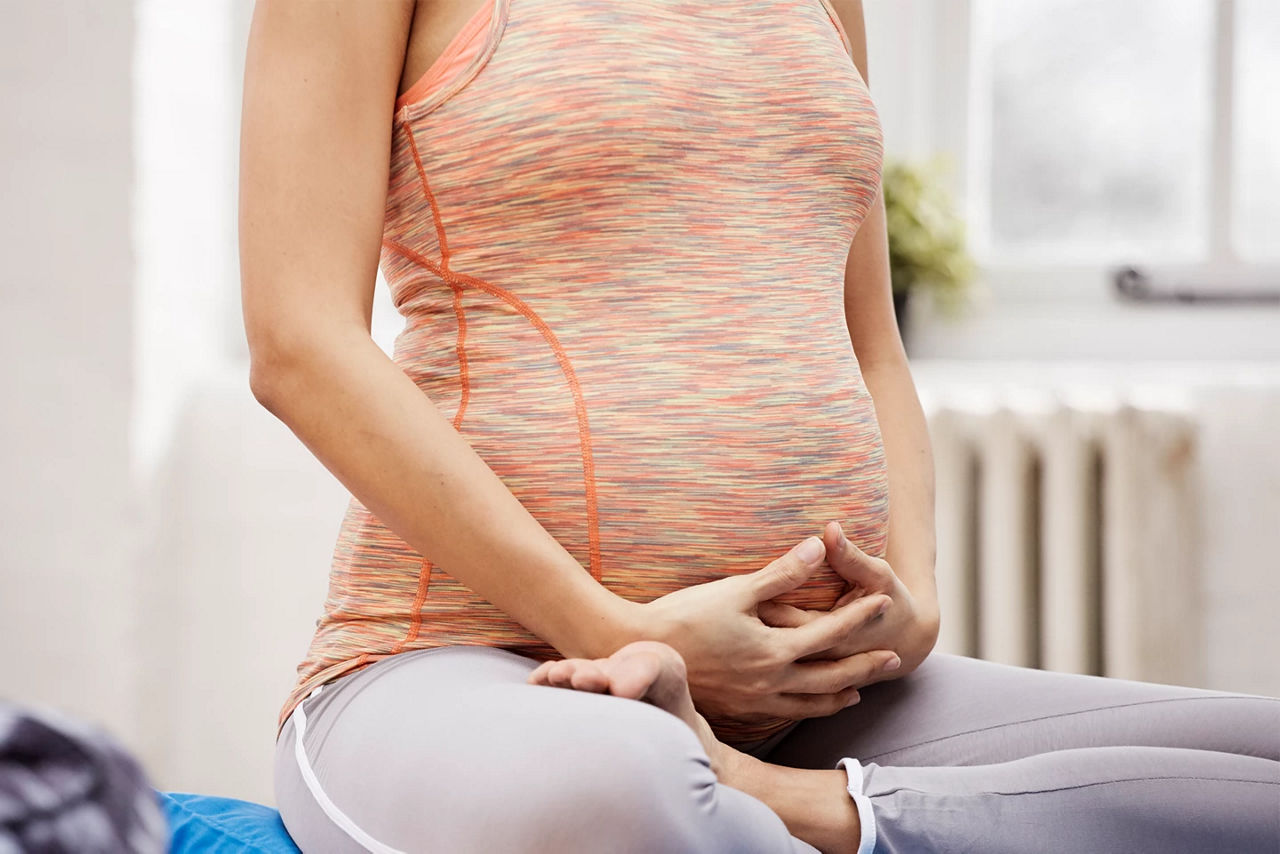

You can perform pelvic floor exercises (also known as ‘Kegel’ exercises) sitting, standing or lying down, although if you’re sitting you may find it less tempting to squeeze your buttocks.
Go for quality rather than quantity (doing it correctly is more important than doing it repeatedly) and check you’re not simply squeezing your buttocks or holding your breath. The squeeze should be internal, and your breathing should remain normal.
Your pelvic floor in pregnancy, birth and post-birth
Your pelvic floor plays a particularly important role during pregnancy and labour2.
Primarily, it supports the weight of your growing baby; the heavier your baby gets, the more these muscles feel the strain. Along with the challenge of supporting such a heavy load, your pelvic floor is also affected by increased levels of relaxin – a pregnancy hormone that softens the muscles and ligaments of your pelvis in preparation for childbirth. As the hormone makes them less effective at holding your bladder, it’s no wonder that some expectant mums experience the odd leak when they cough, sneeze or exercise.
Later on, when labour begins, your pelvic floor helps to rotate your baby’s head into the ideal position, ready for birth. As your womb contracts to push your baby down, the gentle resistance from your stretchy pelvic floor below encourages your baby’s chin to tuck and their head to turn. Once they are in this position, it is easier for their head to pass under the pubic bone, ready for crowning3.
Once your baby’s born, your pelvic floor muscle exercises will help you strengthen the muscles around your bladder, vagina and back passage to reduce the likelihood of incontinence prolapse and help you enjoy a satisfying sex life1.
With regular, simple exercises, you can strengthen your pelvic floor muscles and reduce the likelihood of certain problems later on4.
Pregnant women undertaking pelvic floor muscle training have been found to have a lower incidence of urinary incontinence4 after birth.
Pelvic floor exercises – our top tips
Next steps
- Read more about the benefits of exercise in pregnancy.
- Visit our Active for 2 coach pages to get a running, swimming, yoga and strength training programme tailored to your trimester.
related articles
More sports

Need some help?
You can get quick answers to common questions in our FAQs.
Alternatively, if you need help with general pregnancy or baby advice, or maybe on using or ordering our products - our expert team are always on hand to talk about feeding your baby.
- NHS Choices. What are pelvic floor exercises (Kegel exercises)? [Online]. Available at: http://www.nhs.uk/chq/pages/1063.aspx?categoryid=52 [Accessed: December 2016]. Page last reviewed: 30 April 2017. Next review due: 30 April 2020.
- Ashton-Miller J, Delancey J. Functional anatomy of the female pelvic floor. Ann NY Acad Sci 2007;1101(1):266-96.
- Herbert J. Pregnancy and childbirth: the effects on pelvic floor muscles. Nursing Times 2009;105(7):38-41.
- Boyle R et al. Pelvic floor muscle training for prevention and treatment of urinary and faecal incontinence in antenatal and postnatal women. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 2012;10:CD007471.
- Sangsawang B, Sangsawang N. Stress urinary incontinence in pregnant women: a review of prevalence, pathophysiology, and treatment. Int Urogynecol J 2013;24(6):901-12.
- McKinnie V et al. The effect of pregnancy and mode of delivery on the prevalence of urinary and fecal incontinence. Am J Obstet Gynecol 2005;193(2):512-7.
Last reviewed: 23rd September 2019











